When translating sound waves into electrical signals, synthesizers use voltage. A typical range would be ±15V or ±5V.
For demonstration, I will be using modular synths made with BEAP for Max/MSP. You can download all of the patches here
Outputs signal, but no input other than control voltage.
VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator). Oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input.
ARP 2600:
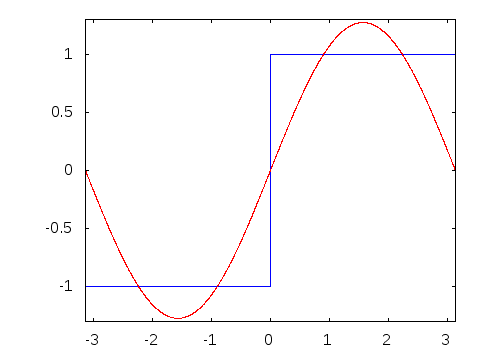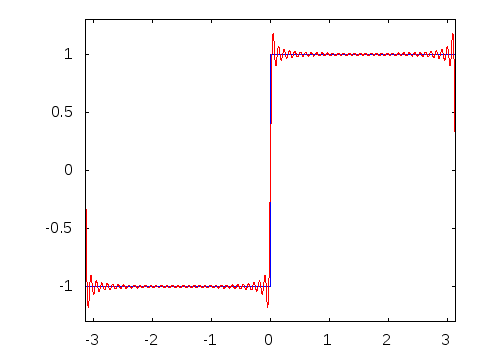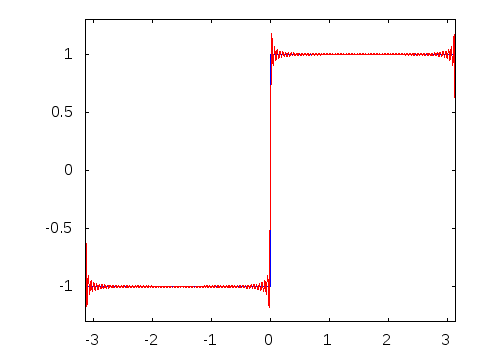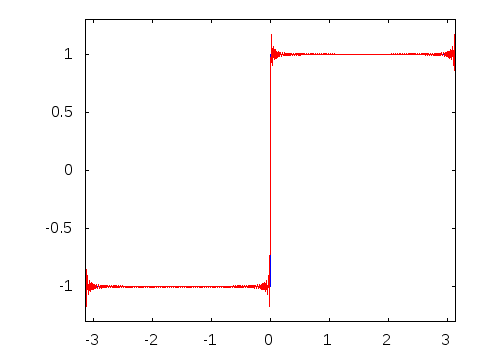
In 1822, Joseph Fourier, a French mathematician, discovered that sinusoidal waves can be used as simple building blocks to describe and approximate any periodic waveform.
Amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. The transition between minimum to maximum is instantaneous for an ideal square wave; this is not realizable in physical systems. Can be represented as an infinite summation of sinusoidal waves

The triangle wave contains only odd harmonics, due to its odd symmetry. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave.
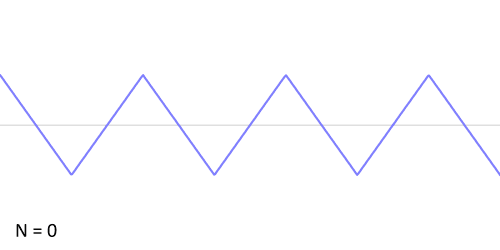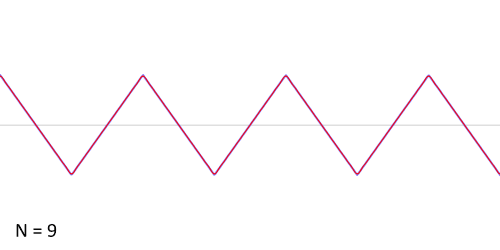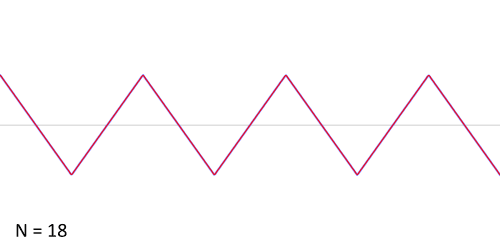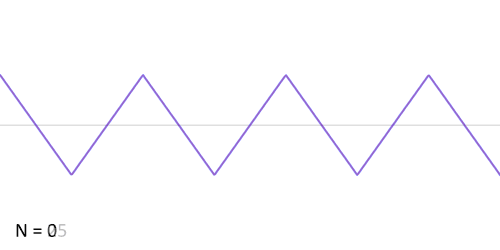
While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave’s sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum contains both even and odd harmonics of the fundamental frequency. Because it contains all the integer harmonics, it is one of the best waveforms to use for subtractive synthesis of musical sounds, particularly bowed string instruments like violins and cellos.

Signal which is used to control a parameter. i.e. Feeding an LFO into the frequency control of a VCO would create a frequency vibrato in which the frequency of the VCO warbles at the rate of the LFO.
Low Frequency Oscillator - slow cycles anywhere from a fortieth of a second to several minutes. Applied as control voltage since it’s not audible.
Voltage Controlled Amplifier. Applying an LFO to VCA would make a tremolo.
Multiple types of noise: white, pink, brown, violet, blue…
This is a control signal which rises and falls. Typically applied to the amplitude of a signal to create discrete “note” events.
A very common synthesizer envelope which models musical instrument notes.
VCF - Voltage Controlled Filter. Attenuates frequencies below (high-pass), above (low-pass) or both below and above (band-pass) a certain frequency
At what frequency the filter starts to attenuate signal.
How quickly the frequency attenuates. Measured as drop in db over octaves.
Delay is an audio effect which records an input signal to an audio storage medium, and then plays it back after a period of time. When this signal is fed back into itself (with some attenuation usually) you get a feedback delay
Chorus is an effect created with a delay which delays and detunes the input audio to thicken the sound.
Compressors narrow the dynamic range (difference between the loud parts and the soft parts) of an audio signal. Typical controls are threshold (above which point the attenuation will occur) and ratio (the amount of attenuation to apply to signal above the threshold value).
Additive Synthesis combines sound generating elements (such as oscillators).
Subtractive Synthesis uses filters to subtract sound from a harmonically rich sound source.